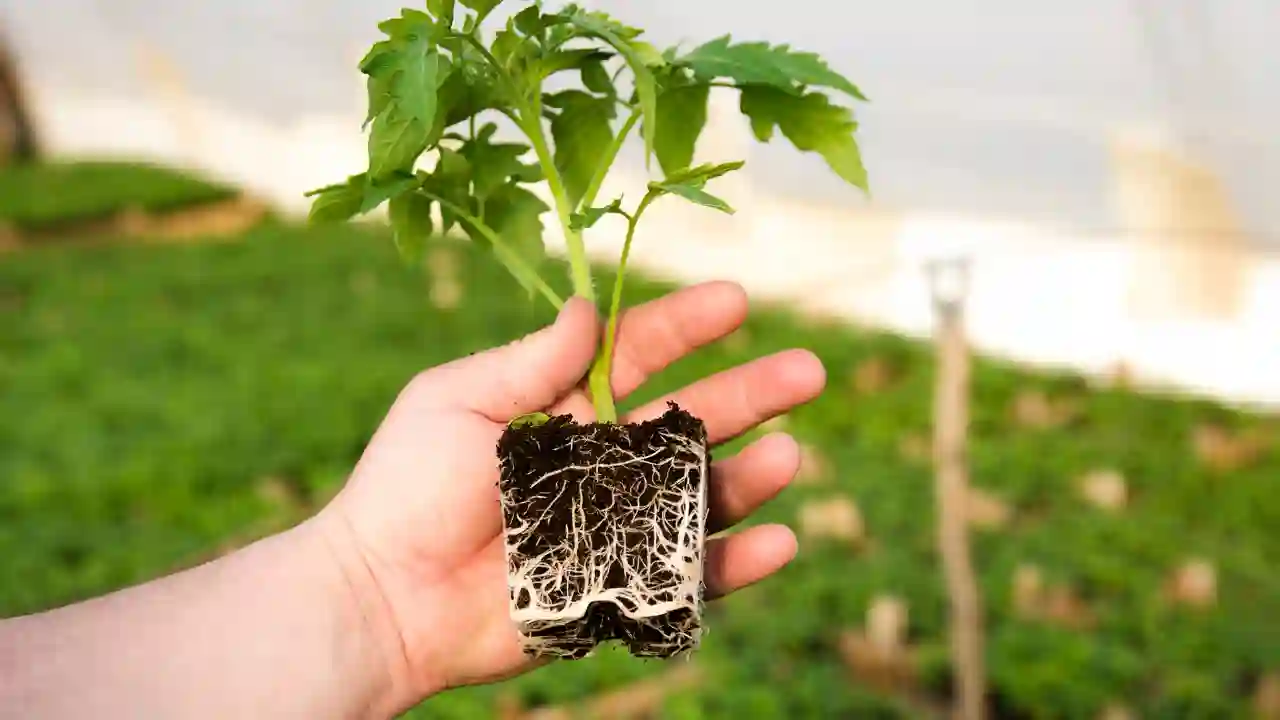
We all know how important roots are for plants, and a plant’s life mostly depends on roots. The plants get their food from the roots, and the same theory goes for tomato plants too.
In short, the taproot of a tomato plant can extend into the soil as deep as three feet, making its presence known in search of hydration and nourishment. Such an extended root system is often observed when it strives to reach abundant essential nutrients for healthy and robust growth.
While planting, most of us focus on steam rather than the root of the plants. But the main factor for good health and growth is how strong tomato plant’s root system is. The deeper the root is, the healthier the plant.
But the roots of different plants grow up to a certain limit. In the case of tomatoes, roots grow a maximum of up to 2 to 3 feet.
This article will guide you through the important factors that affect tomato plant’s roots and how deep they grow.
Factors Affecting Tomato Root Depth

The growth of tomato roots depends on various factors, such as:
- Variety of Tomato Plant
- Container Depth
- Structure of Soil
- Quality of Soil
- Technique Used in Planting
Let’s learn about these factors one by one and how to make a perfect environment for deep roots in tomato plants.
Variety of Tomato Plants:
Mainly there are two different types of tomatoes, determinate and indeterminate.
Determinate tomatoes grow only up to a certain size and ripe in a very short time span. When plants grow their first lot of fruits, they won’t produce new fruits. Determinate plants grow only to a certain extent, while indeterminate tomatoes keep growing during their growing season.
As indeterminate plants grow, they want their taproots to grow deep inside the soil. If the other conditions are favourable for the tomatoes, the root of indeterminate grows deeper than determinate tomatoes.
Container Depth:
Potted tomato roots’ growth depends on the depth of the container in which they are planted, as the taproots can grow maximum till the bottom of the container.
When taproots reach the bottom of the container, they cannot tunnel into the soil. The tap roots are naturally made in such a way that they start growing in a circle in the planted pots, even if they do not get any nutrients or hydration with this process.
Thus we can say that the growth of potted tomato seeds is limited to the depth of the container only.
In the case of a raised bed, when the tap root of tomato plants reaches the bottom, the roots break through its boundaries in search of nutrients and hydration. It happens when the soil quality below the raised bed is excellent.
Soil Structure
As tomato roots are flexible, they can grow in closed-packed and fissured areas. The chances of root development in these areas are very low.
If the roots start growing in such a situation, they will continue to grow like the roots in potted tomato plants.
Quality of Soil:

Soil is the main source of nutrients and hydration for any plant, and tomato plants are no exception. Water and nutrients are passed through the roots to plants for their growth and survival.
For this process, roots need to be planted in excellent-quality soil. The roots don’t need to spread too much to gain nutrients and water for plant growth if already planted in fertile soil.
The roots can also grow in poor soil quality but probably would not get sufficient nutrients and hydration to support plant growth.
If tomatoes are grown in extremely fertile soil, their roots start growing densely, and their energy is used to develop secondary roots, which compromises the development of the taproot itself.
When roots are firmly embedded in healthy soil, the growth of a taproot is significantly hindered due to extra energy being spent on secondary root development. As a result, the overall depth of the root system is substantially reduced by the end of harvest season.
Discover the various nutrients your tomato plant needs to grow and thrive by reading my comprehensive guide on fertilizing tomatoes.
You should also read our another blog on sunlight requirements for tomato plants.
Technique Used in Planting:

Very rare plants grow their roots from stems, and tomato plants are one of them. Utilizing the cutting technique for tomato plants involves deeply ingrowing their stems into the soil and removing up to 60-65% of their lower stem leaves.
With this process, plants do not need any support to grow, which is an added advantage for the cultivator.
In this way, roots start developing from the stem and become capable of delivering adequate nutrients and water to the plant.
Do Tomatoes Have Shallow Roots?
Tomato roots possess both types of roots, i.e., tap and lateral. When tomatoes are grown from seeds, tap roots are developed, growing deep up to 60 Centimetre.
When branches from taproot come out, they are known as lateral roots, which grow only up to 30 centimetres. Thus we can say that tomatoes have both shallow and deep roots.
Tomatoes also develop fibrous roots, which come from their stem. This root develops when you grow tomato plants from cutting. They supply a sufficient amount of nutrients and water to the plant. But when tomatoes are grown from cutting, taproots are traded off and are not developed.
Do Tomato Roots Grow Wide or Deep?
It depends on the type of tomato root, whether it would be wide or deep. Only the fibrous root is different.
When you grow tomatoes from a cutting, fibrous roots are developed, which grow shallow till the plant’s life. When tomatoes are grown from seeds, roots grow wide and deep.
Lateral roots, which are tap roots’ developed stems, grow shallow fibrous root systems. Lateral roots can grow up to 30 centimetres.
When taproots are watered properly, the roots grow densely and up to 60 centimetres. Its growth can be enhanced If watered deeply twice a week.
How Far Do Tomato Roots Spread?
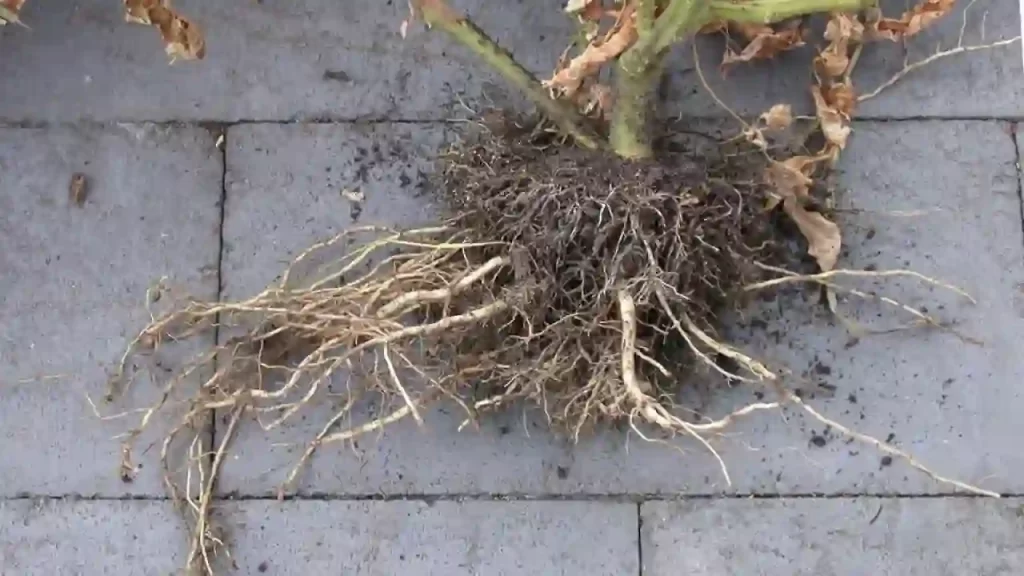

Tomatoes grown from both cutting and seeds and spread their roots about 60 centimetres wide. Lateral roots spread about 30 centimetres wide.
While tomato plantation, airflow should never be neglected. There should be a space of around 60 centimetres between the plants for proper airflow.
- Whether you’re growing a determinate or indeterminate tomato species, the plants roots systems will span up to two feet in width.
- The roots of the plant, or its main root, extend about 12 inches in either direction. This provides a sturdy base for growth and stability.
- To achieve the best airflow, You should plant tomatoes 24 inches (60 cm) apart.
- Your tomato plants’ root systems will extend into the top 12 inches (30 cm) of soil.
- Be gentle when digging around your tomatoes, so you don’t disrupt their delicate roots.
When planting tomatoes, remember that their roots extend 12 inches (30 cm) deep below the surface. Thus, it is essential to be cautious while digging around your plants; use a tiny trowel and carefully observe for any exposed roots – promptly replace them with soil if you discover any.
Special care should be taken while digging around the tomato plants and if roots are uncovered, immediately cover them with soil.
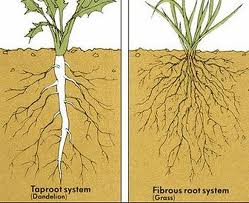
The Structure of Tomato Roots (Tap Root vs. Fibrous Root Systems)
Tomato plants have two kinds of root systems, tap roots and fibrous roots.
Tap root systems are characterized by a single large root that branches out into many smaller lateral roots. This type of root system efficiently absorbs moisture and nutrients from the soil.
Fibrous root systems comprise many thin, branching roots that spread out from the plant in all directions. This type of root system is better at anchoring the plant securely in the soil and absorbing oxygen from the environment.
The structure of each tomato root system varies depending on various factors such as variety, climate, soil conditions, and availability of nutrients.
Generally, determinate varieties have a tap root system, while indeterminate varieties have a fibrous root system.
When you are growing tomatoes in sandy soil, they are more likely to develop taproot system, and those grown in heavier soils may develop both types of roots.
No matter the type of root system, both are important for absorbing moisture and nutrients from the soil to keep your tomato plants healthy and productive.
As a result, you should use proper watering and fertilizing practices to ensure tomato plants have access to all the necessary nutrients for growth. With adequate nutrient availability and good soil conditions, tomato plants can thrive regardless of the type of root system they develop.
Can Tomatoes Grow in Shallow Soil?
For the cultivation of tomato plants, preferably, the soil should be at least 60 centimetres shallow and 30 centimetres deep. If you cannot arrange deeper soil, opt for growing the plant by cutting. This would only help the plant make up for root growth space.
For proper growth and health of the tomato plants, you should arrange excellent quality soil and proper watering.
How Deep Should a Planter Be for Tomatoes?
The minimum depth of the tomato plant is up to 30 Cm, and the maximum depth is 60 CM. If you plan to grow your tomato plants in pots, you should opt for cherry and Grape tomato varieties as they are pot friendly and can grow healthy in pots or containers. Never forget to make a hole at the bottom of your container to ensure a good drainage system.
Always use soil which is rich in nutrients with low nitrogen content. The use of mulch at the time of seeding is highly recommended.
How Much Space Do Tomato Roots Need?
Tomato plants need a minimum of 30 centimetres wide and a maximum of 60 centimetres deep soil.
For taproots, 60 centimetres deep soil is ideal, whereas lateral roots can grow in 30 centimetres deep soil.
Cultivating healthy vegetation necessitates superior-quality soil, appropriately balanced fertilizer, and an effective watering program.
Staking your tomato plants is essential for providing adequate support and maintaining their uprightness, especially when cultivated in shallow soils.
Be extra cautious if you are planning to opt for shallow planting. It requires fertile soil, balanced airflow, sufficient watering and proper support.
How Deep Should My Tomato-Raised Bed Garden Be?
Tomato-raised beds should be at least 8 to 10 inches deep to provide enough space for the tomatoes to grow and develop. However, if you are growing taller varieties that may require more room, making the bed 12 – 15 inches deep is best.
The soil depth should also be considered when planning your raised bed. A good rule of thumb is to ensure the soil depth is at least double the height of your tomato plants.
For example, if you expect your tomato plants to reach six feet tall, you should have 12 inches of soil in the bed. This will ensure they have adequate room to grow and spread their roots.
Additionally, raised beds should be wide enough to accommodate the expected size of the plant when fully grown.
A good guide for width is 40 inches for a single row or 80 inches for multiple rows.
Raised beds should be made with sufficient drainage material and have gently sloping sides to prevent water build-up and pooling.
What Are The Possible Problems With Deep-Rooted Tomato Plants?

Deep-rooted tomato plants are good, but excessively deep roots can cause various challenges to the plants.
Frost:
Tomatoes love the warmth and cannot tolerate cold environments. So they are opted to be cultivated after the frost ends. We often plant tomatoes after the upper surface of the soil is defrosted but fail to understand that the soil inside is still cold.
Planting them deep inside may slow the growth of the plant. As a result, a slowdown in fruiting can be noticed.
Impermeable soil:
If tomatoes are grown in impermeable soil, the chances of water penetration are very less. As a result, the soil drainage system is disturbed, and roots remain soaked in the water.
Due to this, a high chance of root decomposition arises.
You can overcome this problem by giving the plant only the right amount of water.
Clayed Soil:
One of the major factors for tomato plants’ growth is good airflow, and clayed soil is best known for this reason.
Clayed soil can also hold water for a longer period compared to other types of soil. So we do not need to frequently water the plant if it is grown in clayed water.
But the problem arises when the plant experiences heavy rainfall. Due to this, the already grown fruits are damaged due to sudden inflow in them.
Summary
Tomatoes have different root types, which can be grown in both shallow and deep soil. If proper measures are taken, and the above-discussed points are kept in mind, you can grow and enjoy delicious, lovely, tangy tomatoes.
If you’re interested in understanding more and delving deeper into the research, take a look at this experiment in the soil and health library; it’s the most comprehensive assessment of tomato root growth that I’ve seen.